Recent news reports suggest that the generative AI trend may be losing momentum, and Microsoft has initiated a reduction in its orders for Nvidia's H100 AI chips. However, rather than indicating a decline in demand for AI servers, DIGITIMES Research believes that the previous surge was primarily driven by repeated orders. Additionally, as we enter the fourth quarter, major cloud service providers are in the process of planning their capital expenditures for 2024, which means there won't be a substantial increase in new orders. Analyst Jim Hsiao highlights that AI-related service applications are still in their early stages of development. Services like Microsoft 365 Copilot, which require extensive resources, take time to mature. With ongoing technological advancements, the demand for GPU servers appears positive for the next 2-3 years, with the potential for substantial growth thereafter.
The surge in demand for generative AI and large language models (LLMs) has attracted major cloud service providers (CSPs) and leading server brands to participate in the competition for AI servers. Their focus is on high-end AI servers that primarily rely on High Bandwidth Memory (HBM). However, what has caused the bottleneck in the overall shipment of high-end AI servers in 2023? Jim Hsiao analyzes the reasons: currently, the Nvidia H100 GPU is exclusively manufactured by TSMC, and production is constrained due to TSMC's tight capacity for the CoWoS packaging. Orders are expected to be gradually fulfilled in the first half of 2024. Furthermore, there is an issue of insufficient production capacity for HBM, which is used in the H100 GPU. Currently, SK Hynix exclusively supplies HBM3, and Samsung, aiming to secure Nvidia orders, is expected to commence production by the end of this year or early next year.
As a result, Jim Hsiao predicts a gap of more than 35% between supply and demand for high-end AI servers in 2023. Nonetheless, the estimated shipment volume of high-end AI servers is still expected to reach 172,000 units.
Global server shipments from 2022 to 2023 (thousand units)
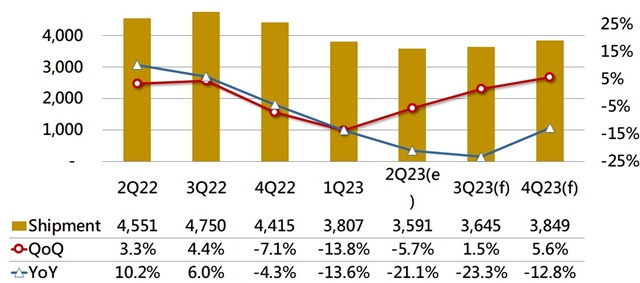
Source: DIGITIMES Research, July 2023
Generative AI has redirected some of the budget allocated for general-purpose servers toward higher-priced AI servers, leading to an overall decrease in general server purchases. In the third quarter of 2023, even though the new mainstream processor platforms are now available, both server brands and cloud service providers have adopted a cautious approach, with expectations of only low single-digit quarterly growth. In the fourth quarter, new products from server brands will continue to gain momentum, and major cloud service providers will start increasing their purchases of both general-purpose and AI servers, resulting in mid-single-digit quarterly growth expectations for overall server shipments.
The budget allocated for general-purpose servers has faced pressure due to the increased demands for AI servers this year. However, in 2024, it seems that preparations for increased capacity will be significant. This includes CoWoS and component preparations, which are expected to grow compared to this year. Consequently, high-end AI server shipments in 2024 are projected to be two to three times higher than this year. This will influence the product planning of Taiwan's original design manufacturers (ODMs) in the high-end segment, also prompting integrated device manufacturers (IDMs) to consider investing more resources in high-end products rather than primarily focusing on mid-to-low-end products.
In the past, data centers had to procure servers from server brand manufacturers such as Dell and HP. However, CSPs now bypass this step and collaborate directly with suppliers like Taiwan's ODM companies, reducing costs associated with intermediaries. This practice is known as ODM-direct. DIGITIMES Research expects that in 2023, high-end AI servers produced through the ODM-direct model will account for 81% of shipments, totaling 139,000 units, while high-end AI servers produced by brand manufacturers will only account for 19%, totaling 33,000 units. Due to high demand for high-end GPUs and orders from major CSPs, most server companies will face limitations in supplying high-end AI servers in 2023. Currently, what server suppliers can do is adopt a hybrid architecture to help businesses provide better hybrid services in the cloud and on-premises.
DIGITIMES Research anticipates that in 2023, over 80% of the global shipments of high-end AI servers from major CSPs and server venders will be concentrated among the top five titans. Microsoft is expected to ship 76,000 high-end AI servers in 2023, accounting for a shipment share of 44.2%, which is higher than the combined shipments of the second to fifth-ranked players (72,000 units).
Top 10 server unit shipments worldwide 2023, by vendor (thousand units)
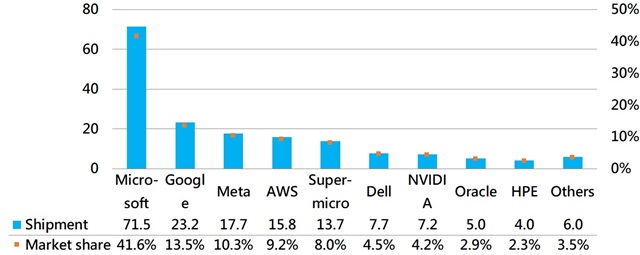
Source: DIGITIMES Research, August 2023
Microsoft, which has invested in OpenAI's ChatGPT and heavily in generative AI cloud services, will lead in direct shipments from contract manufacturers. Google, with a long-term focus on generative AI and expertise in key technologies, will rank second in shipments thanks to its development of TPUs (Tensor Processing Units). Meta will take the third position in shipments. Amazon, while progressing more slowly, actively collaborates with third-party providers and is expected to rank fourth. Traditional brand manufacturers like Supermicro, Dell, Nvidia, and HPE will closely follow the major players.
Jim Hsiao believes that Microsoft has already established a leading position in algorithms and hardware equipment. Unless groundbreaking products in other areas emerge, Microsoft is unlikely to be surpassed, and other competitors will need to exert considerable effort to catch up.
Even before the rise of LLM, Google introduced its own TPU in 2016, distinguishing it from traditional GPUs. CSPs are striving to reduce their reliance on Nvidia, so they are procuring server GPUs from AMD or Intel and investing their resources in developing in-house AI acceleration chips to lower overall costs. The competition in the AI acceleration chip landscape is expected to intensify in the future.
Event announcement
In 2024, the semiconductor sector faces pivotal shifts as demand for silicon wafers varies and global equipment spending adapts. At the forefront of these changes are innovations in High-Performance Computing (HPC) and AI server supply chains. DIGITIMES Asia will spotlight these transformations at the "2024 Next-Gen Intelligence Symposium" on November 3rd, 2023. The event, featuring insights from DIGITIMES' senior analysts Tony Huang and Jim Hsiao along with AI server experts from Supermicro, aims to offer a deep understanding of the evolving tech landscape and Asia's supply chain dynamics.
Register and join us in person at the symposium on November 3rd, 2023, to be part of a pioneering discussion on the AI supply chain and its outlook: https://www.digitimes.com.tw/seminar/DIGITIMESASIA_20231103/
About the Analyst
Jim Hsiao is a DIGITIMES analyst and project manager for the notebook industry and supply chains. His research interests also include the industry, technology, market and applications of artificial intelligence(AI)/deep learning as well as servers and tablets.

Jim Hsiao




